The Labeling of Cortical Sulci using Multidimensional Scaling
Please use this identifier to cite or link to this publication: http://hdl.handle.net/10380/1502
New: Prefer using the following doi: https://doi.org/10.54294/qo3app
Published in The MIDAS Journal - MICCAI 2008 Workshop: Manifolds in Medical Imaging: Metrics, Learning and Beyond.
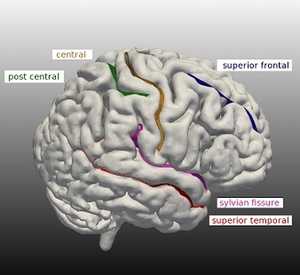
The task of classifying or labeling cortical sulci is made difficult by the fact that individual sulci may not have unique distinguishing features and usually need to be identified by a multivariate feature set that takes the relative spatial arrangement into account. In this paper, classical multidimensional scaling (MDS), which gives a geometric interpretation to input dissimilarity data, is used to classify 180 sulci drawn from the ten major classes of sulci. Using a leave-one-out validation strategy, we acheive a success rate of 100% in the best case and 78% in the worst case. For these more difficult cases, we propose a second stage of classification using shape based features. One of these features is the geodesic distance between sulcal curves obtained from a new open curve representation in a geometric framework. With MDS, we offer a simple and intuitive approach to a challenging problem. Not only can we easily separate left and right brain sulci, but we also narrow the classification problem from, in this case, a 10-class to a 2-class problem. More generally, we can identify a region-of-interest (ROI) within which one can carry out further classification.